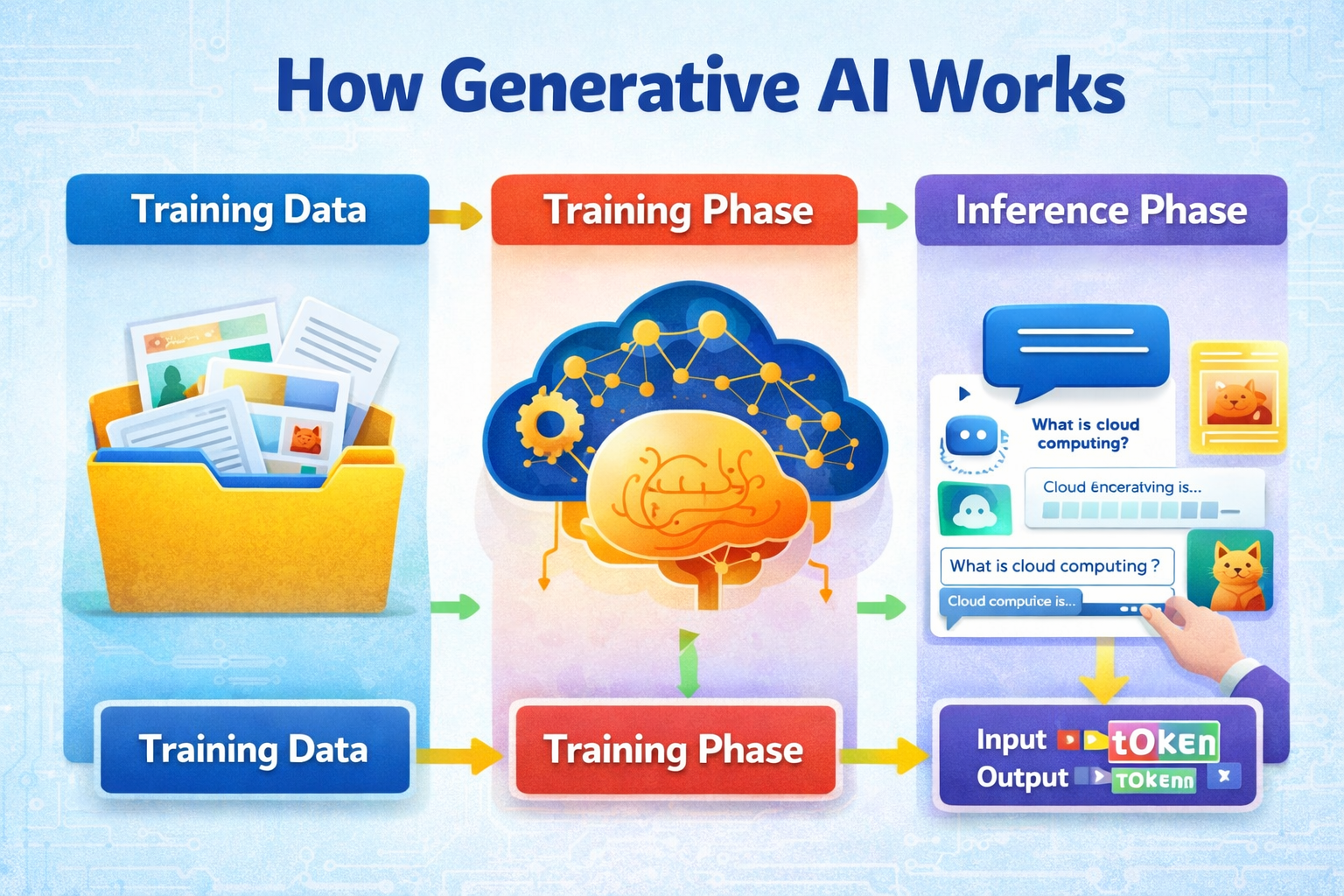
Introduction: Why AI Feels Confusing to Working Professionals
Today, everyone is talking about Artificial Intelligence. We hear terms like AI, Machine Learning, Generative AI, LLMs, and ChatGPT almost daily. Social media is filled with AI success stories, tools, and predictions about jobs. Yet, when working professionals ask a simple question — “Where exactly can I use AI in my current project?” — the answers are often vague.
This confusion is not because people lack intelligence or effort. It exists because most AI content focuses on technology, not application. Engineers, analysts, testers, managers, and architects don’t need more hype. They need clarity.
This blog is written with that goal: to explain how Generative AI is actually used in real projects, in simple language, without heavy math or research jargon.
AI vs ML vs Generative AI – A Simple Explanation
Before jumping into use cases, let’s remove one major mental block.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): A broad concept. Any system that mimics human decision-making.
- Machine Learning (ML): A subset of AI where systems learn patterns from data.
- Generative AI: A newer subset that can generate content — text, code, images, summaries, explanations.
In real projects today, Generative AI is the most immediately useful form of AI for working professionals because it does not require building complex models from scratch.
Think of Generative AI as:
An intelligent assistant that understands context and produces usable output.
The Core Insight: AI Does Not Replace Projects — It Removes Friction
One common fear is that AI will "take over" projects. In reality, that is not how it works today.
Generative AI does not replace your system, architecture, or business logic.
Instead, it helps you:
- Think faster
- Explain better
- Reduce repetitive effort
- Improve clarity
The best way to understand this is by looking at where time is actually spent in projects.
Real Project Areas Where Generative AI Fits Naturally
1. Requirement Understanding & Documentation
Every project starts with requirements — emails, documents, Jira tickets, meeting notes. These are often:
- Unclear
- Incomplete
- Written in business language
How GenAI helps:
- Convert business requirements into technical tasks
- Generate user stories
- Create acceptance criteria
- Summarize long requirement documents
Example: You paste a requirement description into an AI tool and ask:
“Convert this into technical tasks for a backend developer.”
Within seconds, you get structured output that saves hours.
2. Software Development & Coding Support
Generative AI is not a replacement for developers, but it is an excellent co-pilot.
Where it helps:
- Writing boilerplate code
- Explaining unfamiliar code
- Refactoring logic
- Generating sample APIs
Real-world value: Instead of Googling across 5 tabs, developers can interactively ask:
“Explain this function in simple terms.”
This reduces cognitive load and speeds up development.
3. Data Engineering & Analytics Projects
In data projects, a large amount of time is spent not on modeling, but on:
- Understanding data
- Writing queries
- Explaining results to stakeholders
How GenAI fits:
- Generate SQL from plain English
- Explain complex joins or transformations
- Suggest features for models
- Convert analytical results into business-friendly explanations
Key benefit: AI becomes a bridge between technical teams and business users.
4. QA & Testing Workflows
Testing is often repetitive and time-consuming.
Generative AI helps by:
- Creating test cases from requirements
- Identifying edge cases
- Generating regression checklists
This does not remove the tester’s role — it improves coverage and speed.
5. Operations, Support & Internal Tools
Support teams deal with logs, incidents, and repetitive queries.
AI use cases:
- Summarizing incident reports
- Explaining error logs
- Creating internal FAQs
- Drafting post-incident summaries
The result is faster resolution and better communication.
6. Managers & Client-Facing Roles
Managers often spend more time communicating than coding.
Generative AI helps with:
- Status reports
- Client emails
- Presentation outlines
- Meeting summaries
This improves clarity and confidence without changing decision ownership.
A Realistic Example: AI Inside a Project Workflow
Imagine a typical sprint:
- Requirements come from the client
- Tasks are created
- Development begins
- Testing happens
- Status is reported
At each stage, Generative AI can assist:
- Requirement clarity
- Task breakdown
- Code explanation
- Test generation
- Status reporting
The project remains the same — only friction reduces.
Common Mistakes Teams Make With AI
- Trying too many tools at once
- Expecting perfect output without clear prompts
- Treating AI as an answer machine instead of a thinking partner
- Ignoring data privacy and usage guidelines
The most successful teams start small and focus on one use case at a time.
How to Start Using Generative AI Safely at Work
- Use non-sensitive data for experimentation
- Start with internal tasks
- Improve prompts gradually
- Validate output — do not blindly trust
- Treat AI as support, not authority
Why AI Foundation Matters
Many professionals jump directly into tools without understanding fundamentals. This leads to confusion and frustration.
A strong AI foundation helps you:
- Understand where AI fits
- Use tools effectively
- Communicate confidently
- Make informed decisions
That is why foundational learning is critical before advanced adoption.
Closing Thoughts
Generative AI is not magic. It is a practical capability that, when used correctly, improves productivity and clarity across roles.
You don’t need to become a data scientist to benefit from AI.
You only need to understand where it fits in your work.
If you are looking to build that clarity, start small, stay practical, and focus on real use cases.
Explore more insights and learning resources at https://teltam.in/#blogs